2023
Unlocking the Heart Using Adaptive Locked Agnostic Networks
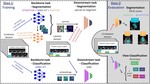
We introduce the Adaptive Locked Agnostic Network (ALAN), a concept involving self-supervised visual feature extraction using a large backbone model to produce anatomically robust semantic self-segmentation. In the ALAN methodology, this self-supervised training occurs only once on a large and diverse dataset. We applied the ALAN approach to three publicly available echocardiography datasets and designed two downstream models, one for segmenting a target anatomical region, and a second for echocardiogram view classification.
Leveraging Synthetic Data for Skin Lesion Analysis
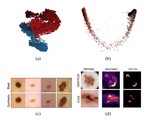
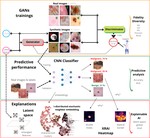
This research delves into the application of unconditional and conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) in both centralized and decentralized settings. The centralized approach replicates studies on a large but imbalanced skin lesion dataset, while the decentralized approach emulates a more realistic hospital scenario with data from three institutions. We meticulously assess the models’ performance in terms of fidelity, diversity, training speed, and the predictive capabilities of classifiers trained on synthetic data. Moreover, we delve into the explainability of the models, focusing on both global and local features. Crucially, we validate the authenticity of the generated samples by calculating the distance between real images and their respective projections in the latent space, addressing a key concern in such applications.
Overcoming Barriers to Data-Driven Workflows in Healthcare and Mobility
This work explores a usability of synthetic data for training visual deep learning models in real-world applications.
Adapting for Swedish AI ecosystem during Eye for AI program 2021-2023
The Eye for AI program is uniquely designed to attract high-performing AI talent with a Master’s or Doctor’s degree and 0-3 years of work experience, typically in the fields of data management, data science and machine learning.
Detect Waste Challenge - Visualize Object Detection on Multi-Source Data
The detect-waste team conducted comprehensive research on Artificial Intelligence usage in waste detection and classification to fight the world’s waste pollution problem.
2022
Assessing GAN-based generative modeling on skin lesions images
We evaluated models’ performance in terms of fidelity, diversity, speed of training, and predictive ability of classifiers trained on the generated synthetic data. In addition we provided explainability through exploration of latent space and embeddings projection focused both on global and local explanations.
Towards Trustworthy Multi-Modal Motion Prediction
We identified the gaps in current evaluation methodologies and proposed a more comprehensive and holistic evaluation framework for multi-modal motion prediction autonomus vehicle system.
Handling sign language transcription system with the computer-friendly numerical multilabels
We designed an automated tool to convert HamNoSys annotations into numerical labels for defined initial features of body and hand positions.
Trustworthy AI for decision support in dermatology
We explained the classifier’s diagnosis for skin cancer using both local and global techniques of explainable AI.
HearAI - Where AI Supports Inclusion of Deaf and Hearing-Impaired Individuals
In the HearAI non-profit project, we investigated different multilingual open sign language corpora labeled by linguists in the language-agnostic HAMburg NOtation SYStem.
Advantages and Limitations of Sign Language Corpora for Sign Language Recognition
In our solution, we proposed computer-friendly numeric multilabels that greatly simplify the structure of the language-agnostic HamNoSys without significant loss of glos meaning.
HearAI - Non-Profit Project for Sign Language Recognition
In the HearAI non-profit project, we investigated different multilingual open sign language corpora labeled by linguists in the language-agnostic HAMburg NOtation SYStem.
Improving Swedish healthcare ecosystem using Flower
Sahlgrenska Hospital, Region Halland and AI Sweden have decided to lead an effort of applying Federated Learning in practice. For this use case we made use of the SIIM-ISIC 2020 dataset and performed two main tasks. First, melanoma detection, and second, skin lesion image generation.
Deep diving into synthetic data use in healthcare
The use of healthcare data in the development of DL models is associated with challenges relating to personal data and regulatory issues. Patient data cannot be freely shared and is therefore limited in its usefulness for creating AI solutions. All of these issues can be addressed using different methods, showing the potential of artificial data for such use cases.
Synthetic data generation in healthcare
Neural networks can be applied to distinguish between melanoma and non-melanoma cases in a few seconds, which makes it a great help to the diagnosing physician.
2021
Deep neural networks approach to microbial colony detection—a comparative analysis
We compared the performance of three well-known deep learning approaches for object detection on the AGAR dataset, namely two-stage, one-stage, and transformer-based neural networks.
Modelling Arbitrary Complex Dielectric Properties—an automated implementation for gprMax
We developed a new module within gprMax that can be used to simulate complex dispersive materials using multi-Debye expansions in an automatic manner. The module is capable of modelling Havriliak-Negami, Cole-Cole, Cole-Davidson, Jonscher, Complex-Refractive Index Models, and indeed any arbitrary dispersive material with real and imaginary permittivity specified by the user.
Waste detection in Pomerania - non-profit project for detecting waste in environment
The detect-waste team conducted comprehensive research on Artificial Intelligence usage in waste detection and classification to fight the world’s waste pollution problem.
Numerical modelling of conical wave formation in multimode optical fibers
In this work, we present the results of numerical modelling of nonlinear pulse propagation in multimode optical fibers leading to discretized conical emission.
2019
Modes classification in multimode optical fibers with a deep learning network
The field distribution of the same mode could be slightly different depending on wavelength and reflective index profile. To exhibit a dispersion characteristic for multimode fibers over a wide spectral range, a verification of refractive index value for a particular mode at a specific wavelength is needed.
Counting and classification of bacterial colonies using deep learning
Counting bacterial colonies is a fundamental task in microbiology. Currently, manual counting remains the gold standard. This is a timeconsuming and error-prone process, which requires a trained professional. To avoid these issues, the automated method can be applied for the task. The goal of our work was to design a model that counts and classifies bacterial colonies in Petri dishes using RGB images.
Ultrashort pulse propagation and conical emission in multimode optical fibers
There is an urgent need of clarifying the potential and areas of applicability of numerical models to facilitate the accurate design of future nonlinear and multimode fiber devices. Therefore we performed the simulations of conical emission using two well-known numerical tools, namely, the unidirectional pulse propagation equation and the multimode generalized nonlinear Schrodinger equation.
2018
Normal dispersion supercontinuum reaching mid-infrared in silica microstructured optical fibers
Our simulations show that all-normal dispersion supercontinuum generated in optimized microstructured fiber (with hexagonal and kagome geometry) covers whole transparency window of silica glass.
The influence of attenuation on a self-organized second harmonic generation in a germanium doped microstructured silica fiber
We extended a theoretical model of self-organized SHG to include an attenuation and investigated the influence of fiber loss on the self-organized SHG process.